
3. Setting the Scene Cleaner air for Scotland the road to a healthier future gov.scot
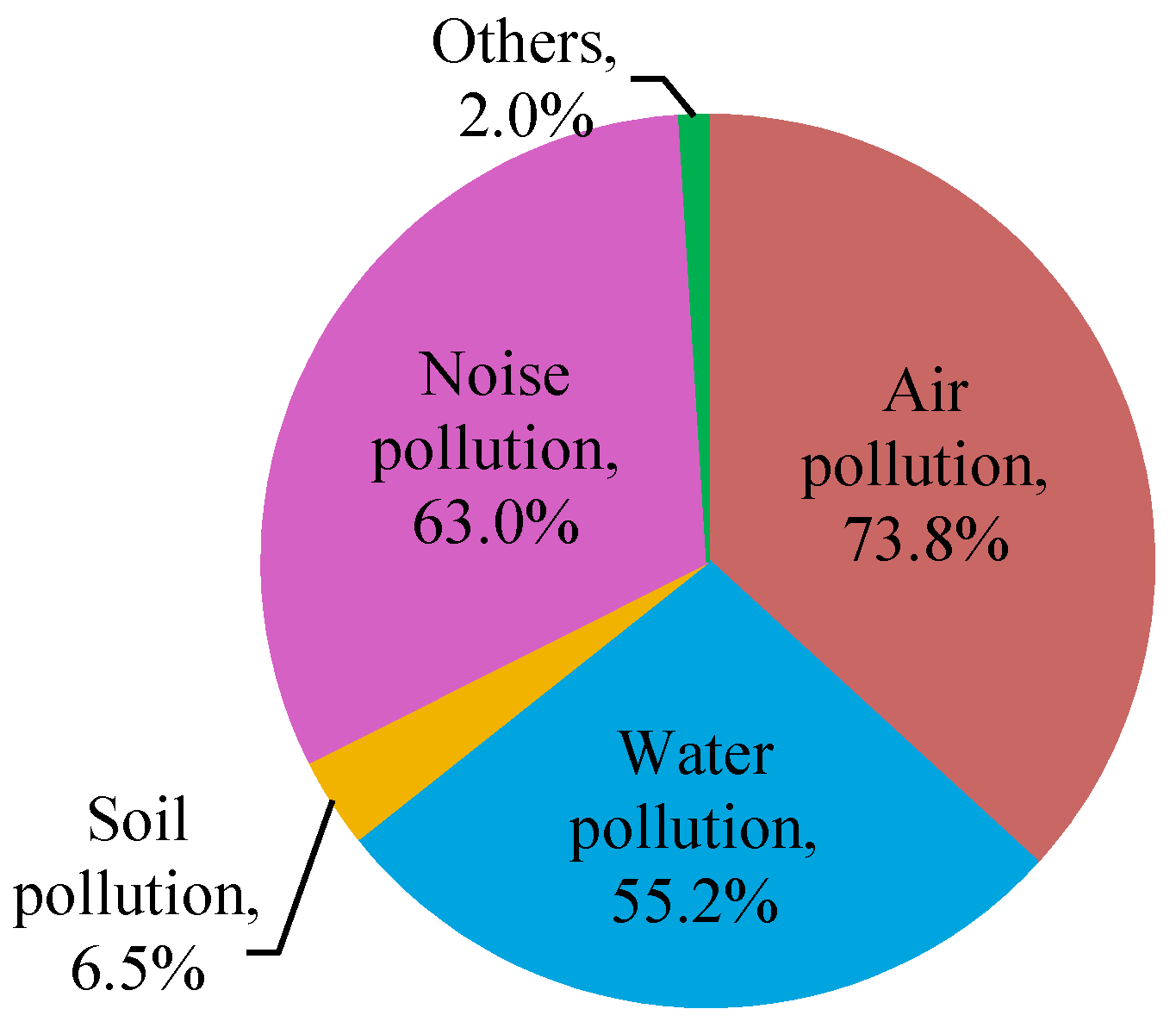
Broadly, environmental pollution consists of six basic types of pollution, i.e. air, water, land, soil, noise, and light. When people think of environmental pollution, most focus on fossil fuel and carbon emissions, but there are different contributing factors. Chemical pollution in bodies of water contributes to illnesses.

4.2. Ecosystems impairment caused by soil pollution
Air Pollution Includes Gases and Particles. Air pollution consists of gas and particle contaminants that are present in the atmosphere. Gaseous pollutants include sulfur dioxide (SO 2), oxides of nitrogen (NO x), ozone (O 3), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), certain toxic air pollutants and some gaseous forms of metals.Particle pollution (PM 2.5 and PM 10) includes a.

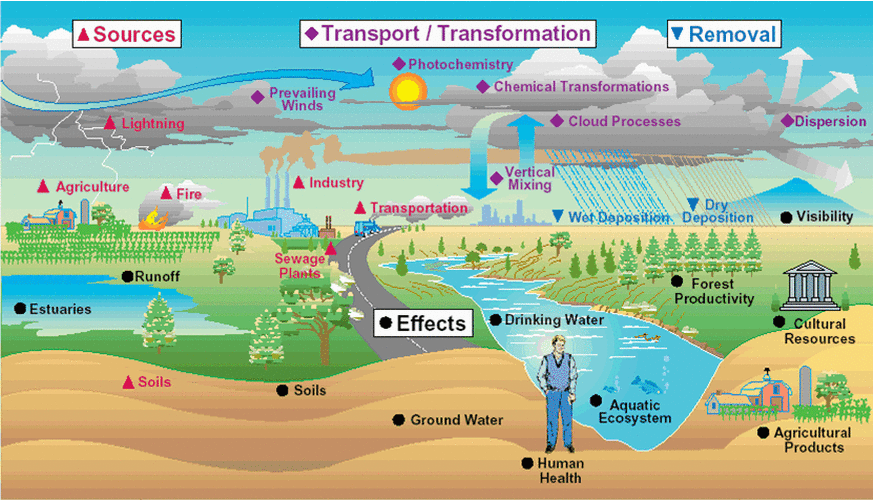
Clean Air Hub The Basic Facts Where does air pollution come from?
Air Pollution Our overview on both indoor and outdoor air pollution. By Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser This article was first published in October 2017; last revised in January 2021. Air pollution is one of the world's largest health and environmental problems. It develops in two contexts: indoor (household) air pollution and outdoor air pollution.

Pin by Nathan Hoffman on Soil Pollution Industrial waste, Oil industry, Power plant
"Pollution is the introduction of substances (or energy) that cause adverse changes in the environment and living entities ." Pollution need not always be caused by chemical substances such as particulates (like smoke and dust). Forms of energy such as sound, heat or light can also cause pollution.

{LaB} » Sources of Pollution
Land pollution Editor's Picks Current statistics on this topic Emissions Most polluted countries based on PM2.5 concentration globally 2022 Emissions Air pollutant emissions in the U.S..
What is Pollution! Green Revolution NGOPollution
Pollution is defined as the introduction of harmful contaminants into the environment that negatively alters our surroundings. The widespread prevalence of environmental pollution began with the.
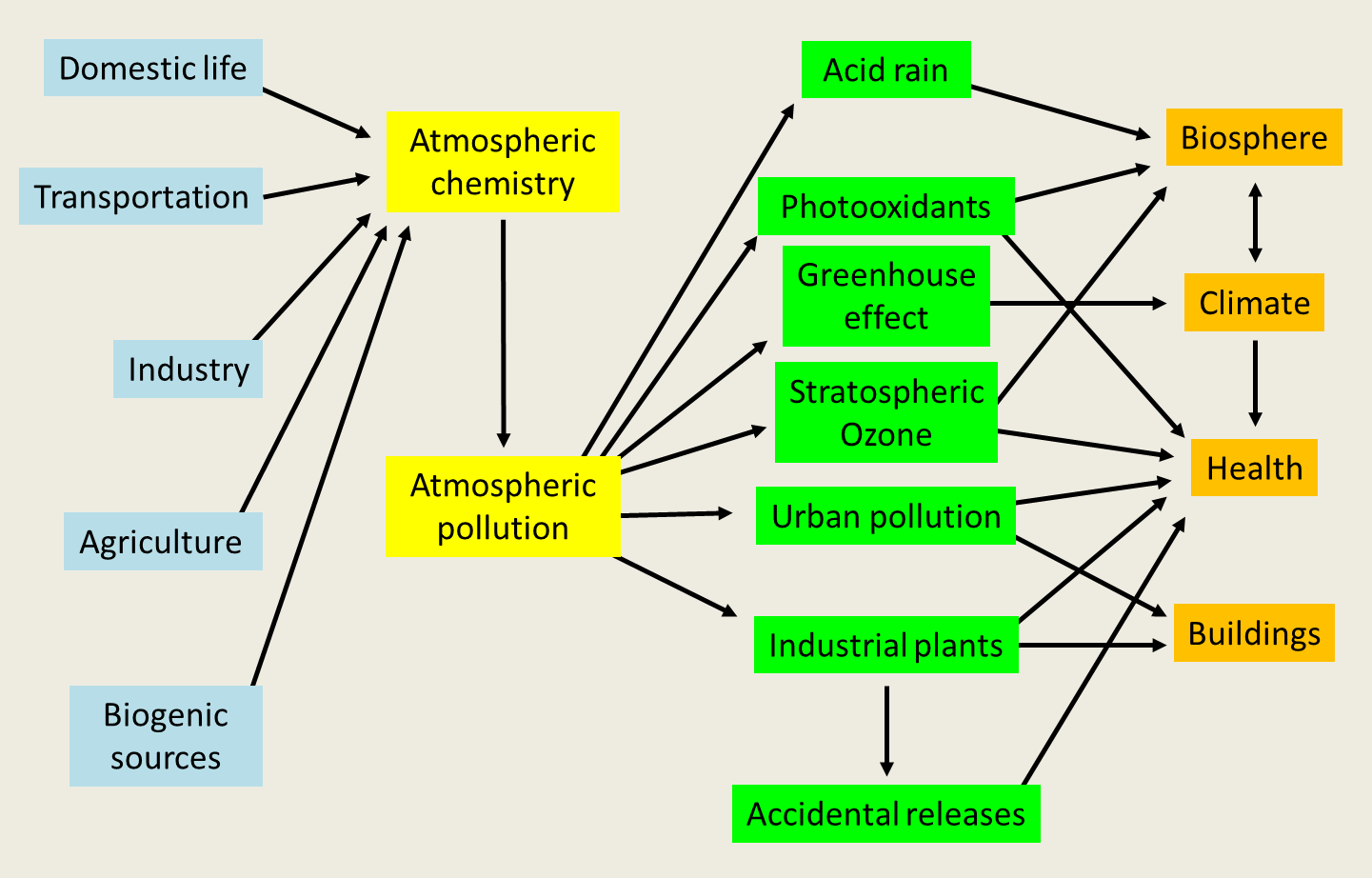
Air pollution Encyclopedia of the Environment
pollution, the addition of any substance ( solid, liquid, or gas) or any form of energy (such as heat, sound, or radioactivity) to the environment at a rate faster than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form. The major kinds of pollution, usually classified by environment, are air pollution, water.

Lesson 6.04 Air Pollution
THERMAL POLLUTION. Thermal pollution is the addition of heat to a cool environment, and it is caused by water or air used as cooling fluids in power plants and manufacturing that becomes heated in the process. Heated cooling water from power plants may be 15 ˚C (27 ˚F) hotter than lake or stream water, which increases metabolic rates in.
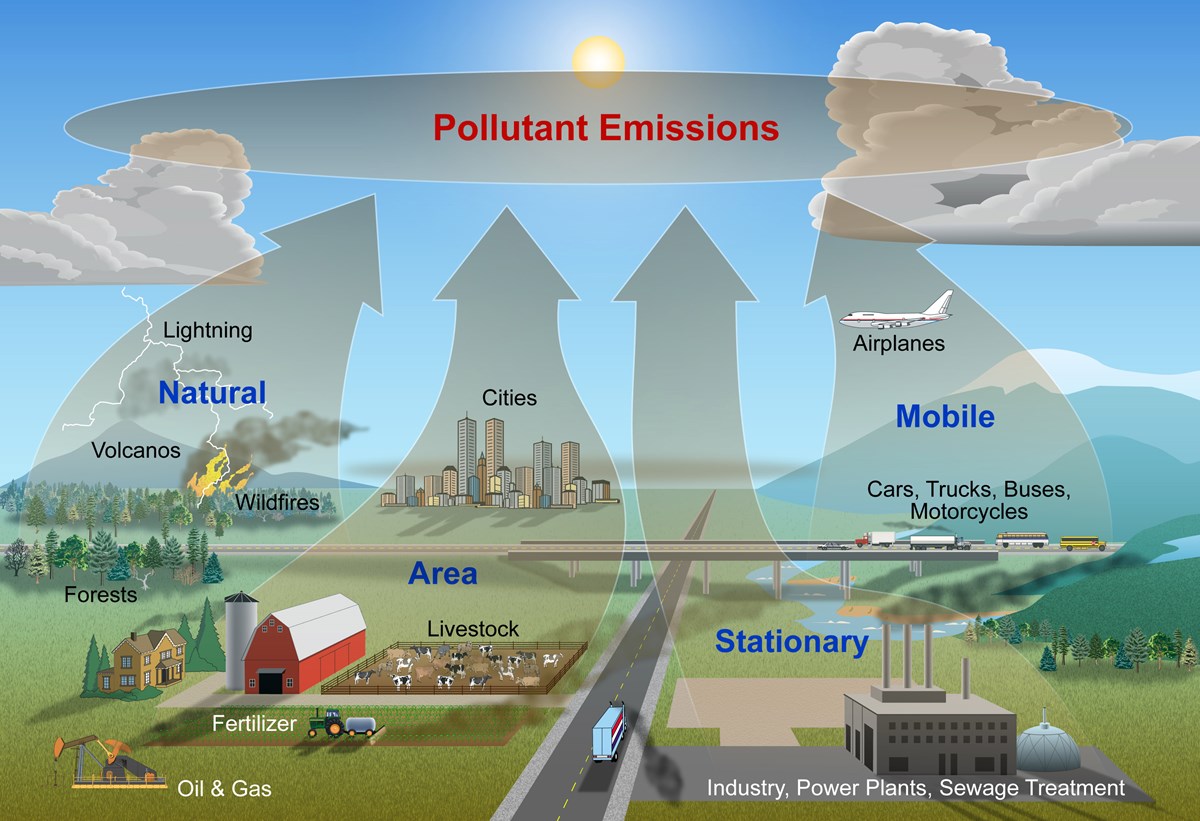
Where Does Air Pollution Come From? Air (U.S. National Park Service)
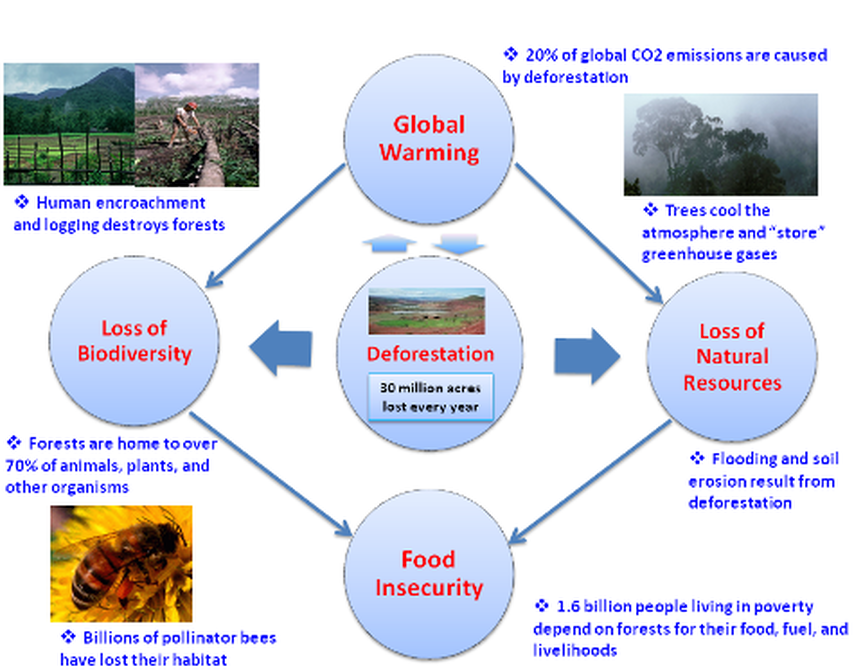
Over the course of the twentieth century, growing recognition of the environmental and public health impacts associated with anthropogenic activities (discussed in the chapter Environmental Health Hazards) has prompted the development and application of methods and technologies to reduce the effects of pollution.In this context, governments have adopted regulatory and other policy measures.
What Is Environmental Pollution Environmental Pollution Mapa Mental North carolina division
In this and the next study session we will look more closely at pollution. In this session you will learn about the different types and sources of pollution and the various human activities that can cause pollution. We will also describe the ways pollution can affect different sectors of the environment: water, air and soil.

Types of environment pollution Royalty Free Vector Image
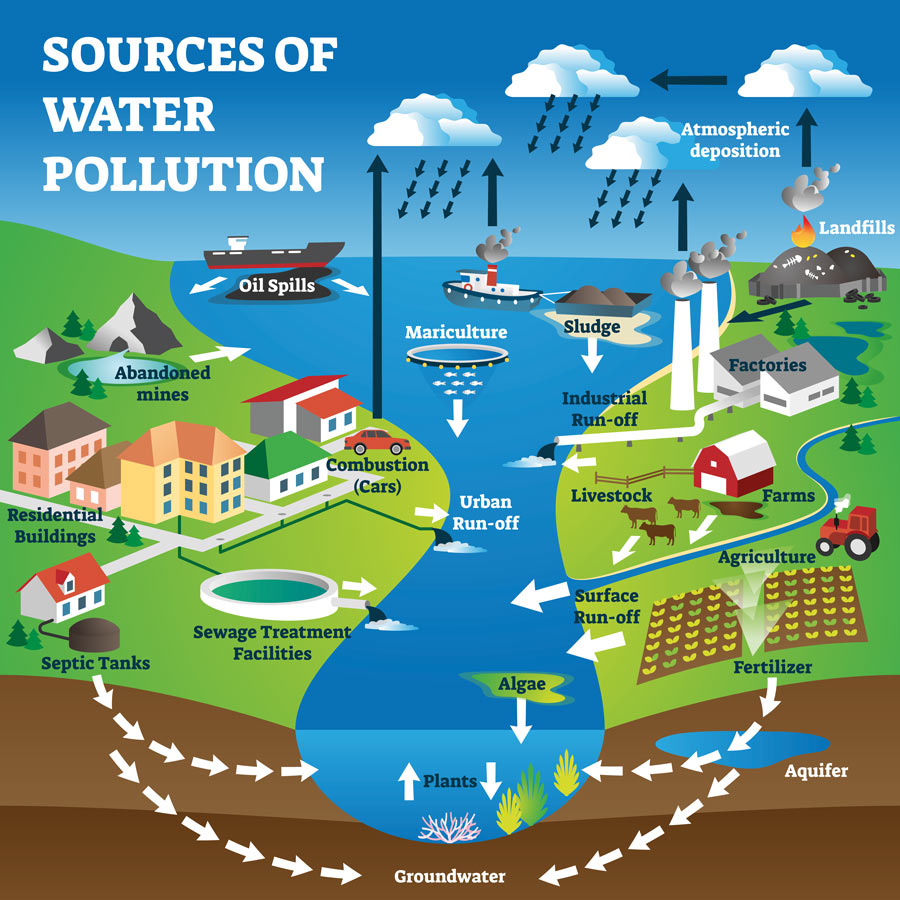
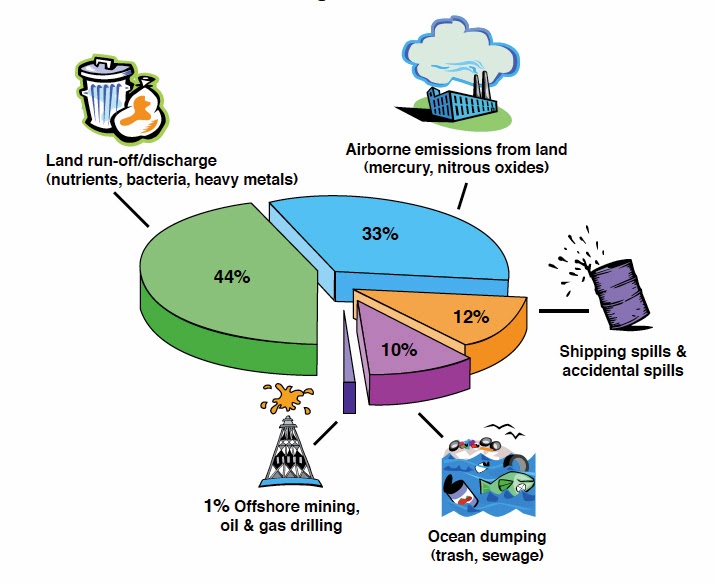
water pollution, the release of substances into subsurface groundwater or into lakes, streams, rivers, estuaries, and oceans to the point where the substances interfere with beneficial use of the water or with the natural functioning of ecosystems. In addition to the release of substances, such as chemicals, trash, or microorganisms, water.

Natural Resources Types & Importance Environmental Pollution Measures
Air pollution, release into the atmosphere of various gases, finely divided solids, or finely dispersed liquid aerosols at rates that exceed the natural capacity of the environment to dissipate and dilute or absorb them. High concentrations can cause undesirable health, economic, or aesthetic effects.
Solving soil and groundwater contamination Research Outreach
Pollution is a negative externality. Economists illustrate the social costs of production with a demand and supply diagram. The social costs include the private costs of production incurred by the company and the external costs of pollution that are passed on to society. The diagram below shows the demand and supply for manufacturing refrigerators.
pollution
Article Full-text available Sep 2019 Azhar Alhadad Zahraa Abdulmuati Alghadhban Halima Zugair Hussain ABSTRACT: During the past two decades, the issue of environmental pollution has received.
Entertainment Diagrams
Pollution and Pollutants. Pollution is any unfavorable alteration in the physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of our environment, including the air, water, and soil, that may or will have a negative impact on people or other species as well as the life support systems of our biosphere. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic.

Types of Pollution Pollution Video Compilation Pollution Video YouTube Types of
The concept of monitoring of air quality by plants is a well-established fact. The plants used for this purpose are termed indicator plants. It is known that some plants are very sensitive to air pollutants; they are thus used as indicator species for bio monitoring of air quality. In recent years, increasing efforts are being made to use.