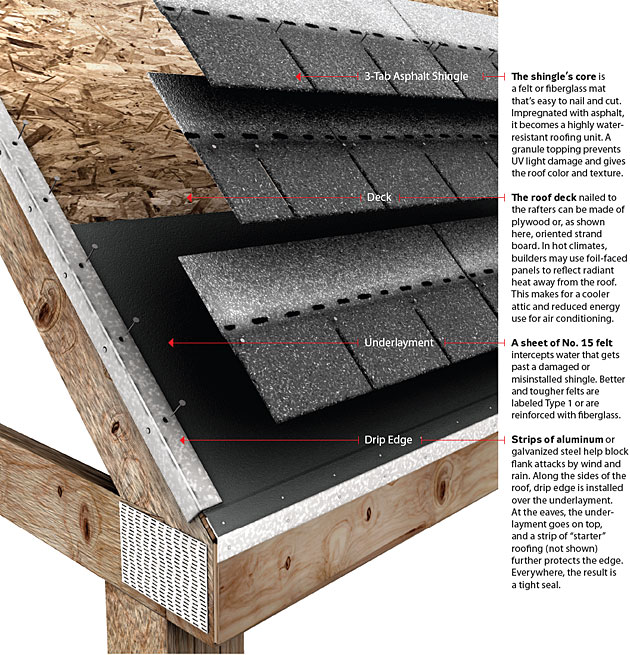

Layers of a Roof Frisco Roofing Company Lifetime Fence & Roofing
This roofing layers diagram shows the layers that sit directly under the shingles plus the added protection for the edges of the roof. Diagram showing roofing layers for a residential house Framing - includes the roof trusses that sit at the top of your house and support the weight of all the materials used to build your roof.
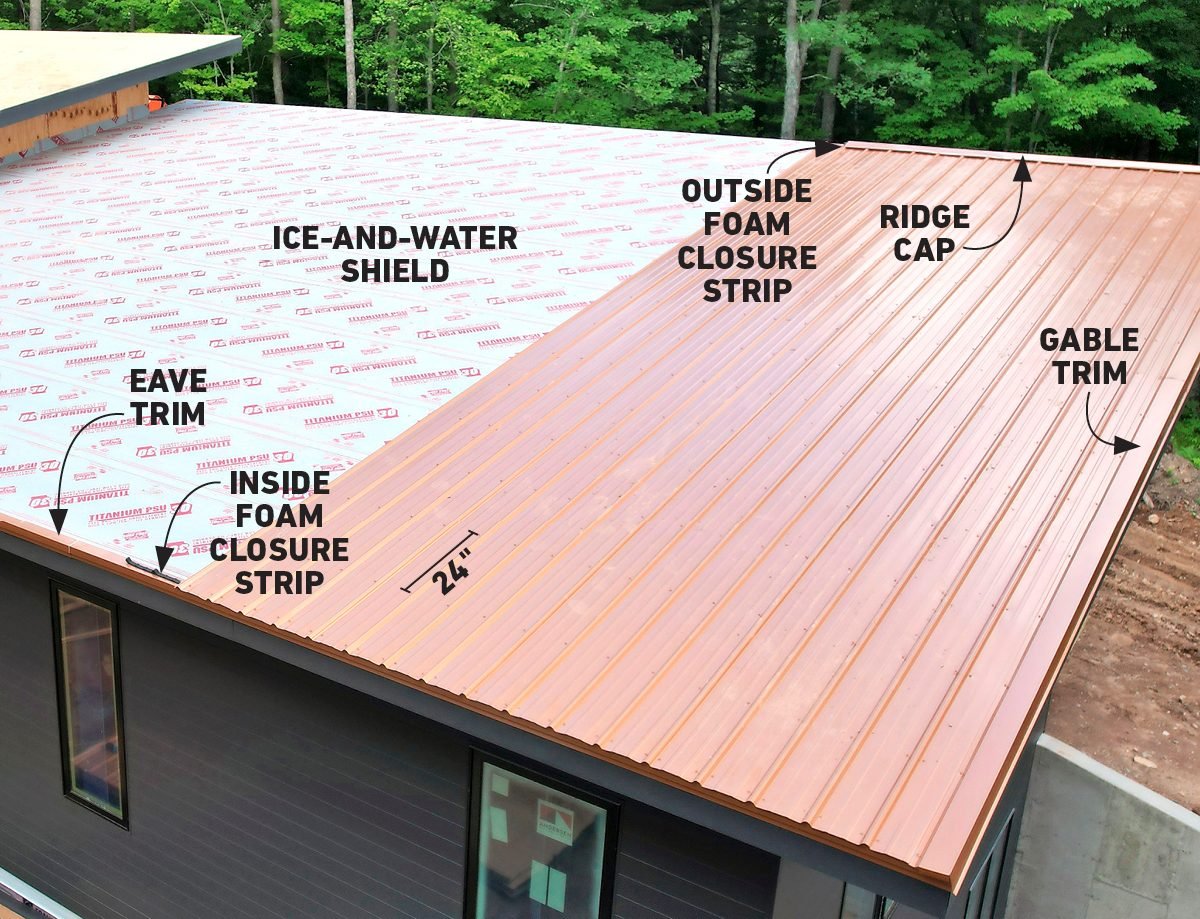

A Full Guide to Metal Roof Installation (DIY) Family Handyman
Layer #2 - The Drip Edge. Most of the crucial components of any residential roof are made of wood. As you know, wood is organic and, therefore, susceptible to rot and water damage. A drip edge is required to protect the vulnerable areas of your roof (the fascia, the roof decking, the areas behind your gutters, etc.).

Metal Roofing BC Services
Roofing Underlayment: Roofing underlayment is a layer of material, usually synthetic or felt, that adds extra protection on top of the roof deck and under the shingles. Synthetic underlayment helps repel moisture and provides protection against water infiltration. Synthetic underlayment is becoming a popular material choice over felt due to.
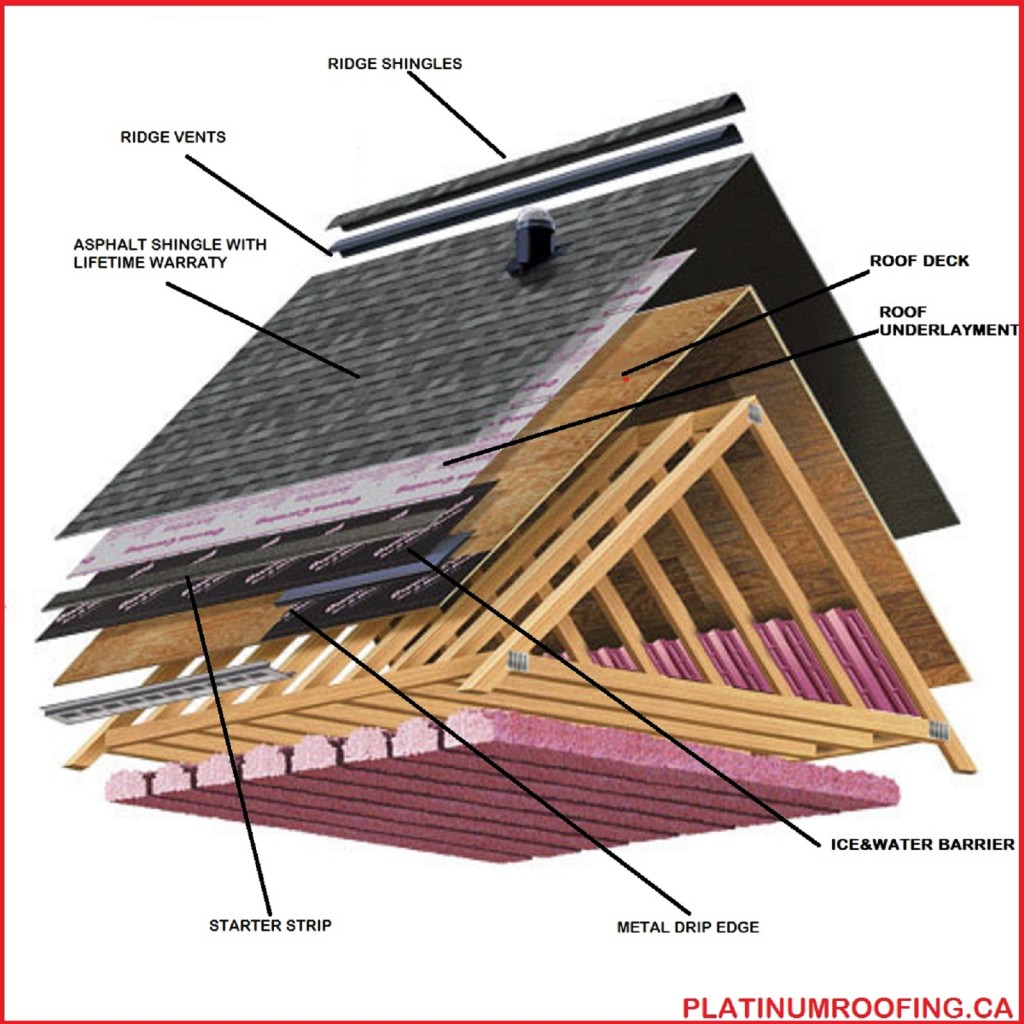
Residential Roof Replacment Calgary Platinum Roofing
Diagram: Anatomy of a Roof - common parts and layers of a residential roof with asphalt shingles. What are the Common Parts of a Roof? 1. Roof Ridge: The ridge of a roof is the horizontal line running the length of the roof where the two roof planes meet, often called the peak of the roof. Hip and ridge shingles are specifically designed to.

Understanding The Layers of a Roof and Why They Are Important All
Here's how to build temporary bracing for your roof trusses: Cut blocks of 2×4 lumber to span from the top chord of one truss to the top chord of another truss. Nail the bracing into the top chords while still following the manufacturer's layout. Install diagonal bracing in a "W" pattern.

Environmentally Friendly Green Space Roofs The New Urban Frontier
Roofing Underlayment: Roofing underlayment is a layer of material, usually synthetic or felt, that adds extra protection on top of the roof deck and under the shingles. Synthetic underlayment helps repel moisture and provides protection against water infiltration. Synthetic underlayment is becoming a popular material choice over felt due to.
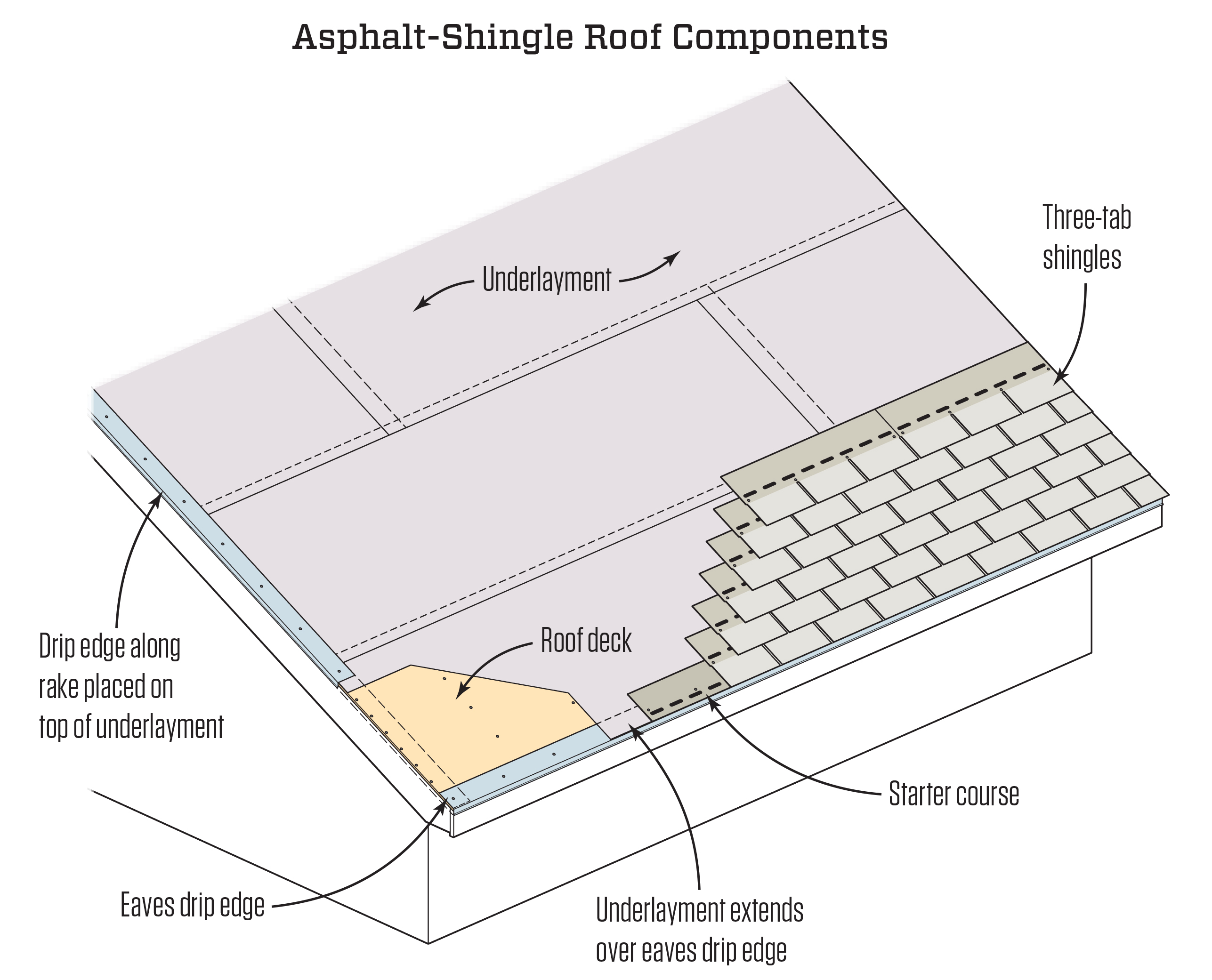
Asphalt Roof Shingling Basics JLC Online
Each layer is a ply, and a roof has multiple plies depending on the climate and specific roofing details. Diagram of Built Up Roofing Layers Generally, installation starts with a base sheet that can be mechanically fastened if there is any slope to the roof — there should almost always be a minimal slope to assist with drainage.

Residential & Commercial Roofing Infinite Roofing Albany, NY
In this article, we will talk about the different layers of the roof and their functions. Without further ado, let's break down each aspect of a roofing system. Parts of a Roof Diagram. Before we dive in, let's get a look at a roofing structure diagram so we can visually map the roof part names to the physical roof pieces.
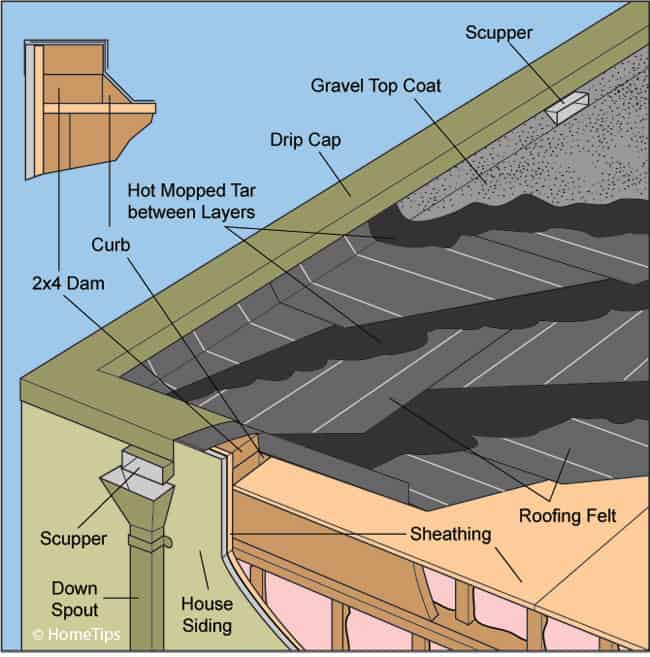
BuiltUp (TarandGravel) Roofing Systems HomeTips
Asphalt shingles or another type of roofing material. This is the layer that most people think of when talking about a roof. This is the top layer of your roof system and will be the type of roofing material you choose (asphalt shingles, metal roofing, cedar shake roofing, synthetic roofing, etc.) It will make up the bulk of your roof, and it.

Parts to a Roof Terms You Need to Know When Talking to a Roofer
Diagram of a Roof Anatomy. When we look at a roof, we can distinguish three types of parts: the structural elements, the decorative parts, and the ventilation parts.. made from felt or some other organic, thick fabric. This is then stacked in layers on top of the decking. The number of layers used will determine the degree of heat insulation.

Roofing layers Page 1 Homes, Gardens and DIY PistonHeads UK
5. Ridge. A roof's ridge is found in specific types of roofs such as mansard, gambrel, gable, and pitched. Pitched roofs are very common among suburban homes, forming the classic upside-down 'V' shape. The ridge is located at the uppermost point of the roof, at the point where the two opposing sides connect.

20 Important Parts of a Roof (And How They Protect Your Property)
Here is a diagram of a typical warm roof: Flat Roof Designs For Houses. There is a wide variety of flat roof materials available, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. The following outlines ways to build, protect and reinforce your roof.. Alternating layers of roofing felt (usually fiberglass) and hot-applied asphalt;

19 Parts of a Roof on a House (Detailed Diagram)
The general purpose of roof ventilation is to encourage natural airflow through the attic space to keep it at a uniform temperature and humidity level. Ventilation systems consist of intake and exhaust vents installed at strategic intervals in the roof or attic. Common types of vents include ridge vents, gable vents, and static vents.

How To Understand The 8 Layers Of Your Roof Straight Line Roofing
A starting layer of shingles lines the edge of every home's roof. The starter strip is laid down underneath the underlayment to seal the edges of the roof. The purpose of this layer is to defend the rest of the roof against strong winds and reduce blow off. Shingles. The most obvious layer of protection on your roof is the layer of shingles.

Image result for metal roof layers Roofing Screws, Metal Roofing
Ridge Board: A horizontal timber or metal resting at the peak of the roof. The rafters and trusses are connected to the ridge board for a cohesive framework. Solid Decking: A composite decking made of solid materials. It resembles real wood and particularly strong and stable for bearing heavy load. Felt Underlayment: It is a waterproofing layer.

Platinum Protection Roofing System Limited Warranty (NonResidential
Panelised roofing such as SIPs (structural insulated panels) uses large pre-insulated sheets, laid across roof beams. The beams will typically be placed along the ridge, at the eaves and halfway between the two where they are known as purlins. Once the purlins are in place, the panels can be craned in in a matter of minutes.